ISOCYANATE

INTRODUCTION
Isocyanates represent a class of chemicals that are characterized by high reactivity and versatility. The most chemically relevant attribute of isocyanate chemistry is its reactivity with molecules having active hydrogens but their significance is usually in the context of their relationship to polyurethane polymerization and structure. The two highest volume aromatic isocyanates are based in one case on toluene to make toluene diisocyanate known as TDI and in the other case aniline and formaldehyde to make methylenebis ,phenyl isocyanate, commonly referred to as MDI or PMDI.
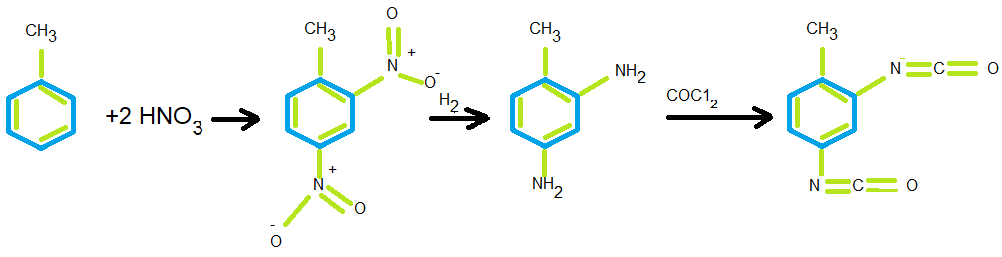
Toluene Diisocyanate ( TDI)
toluene diisocyanate is one of the Aromatic Diisocyanates that production of TDI begins With nutrition of toluene , which is subsequently hydrogenated to the polyamine . The last step is a reaction of the amine with phosgene to make TDI. The most common form of TDI offered commercially is an 80/20 mixture of the 2,4- and 2,6-isomers but is also available as a 65/35 mixture as well as a pure 2,4-isomer. The main outlet for TDI is in the manufacture of polyurethane (PU) flexible foams used in furniture, bedding and automotive and airline seats.

This is achieved by the reaction of TDI with a polyol to produce the foam. Smaller uses for TDI include PU elastomers and coatings. Despite PU coating relatively high cost, they are suitable for a range of high performance applications due to their excellent durability, resistance to corrosion and abrasion, and flexibility.
Diphenylmethane Diisocyanates (Mdi)
MDI is produced from aniline and formaldehyde feedstocks, Thus, the economics of aniline and MDI production are very tightly correlated and dependent on each other. The largest volume uses for MDI are rigid foams, adhesives, sealants, coatings, elastomers, and flexible polyurethane foam. Rigid foam applications monopolize about 60% of the total MDI volume. It is also used to make many types of footwear, sports and leisure products and to a much lesser extent, some specialty flexible foams. MDI can also be used as a binder for wood and to produce mold cores for the foundry industry.

Aliphatic Isocyanates
with the exception of TDI and MDI that are Aromatic isocyanates , aliphatic isocyanates also are produced . The vast majority of aliphatic isocyanates are used for coatings. This application particularly takes advantage of the reduced weather-induced coloring of aliphatic-based urethanes versus aromatic-based polyurethanes . However, along with weathering, coatings often must also provide other properties such as optical clarity,a high glass transition temperature, and barrier to a variety of chemicals the coating may encounter in use. Additionally, a small amount of aliphatic isocyanates is used in thermoplastic polyurethane films that are also used for weatherable applications. Almost 90% of aliphatic isocyanates are used in coatings and 6% in elastomers. Almost half of the polyurethane coatings that use aliphatic isocyanates are automotive related. The need for aliphatic isocyanates stems from the photooxidative instability of aromatic isocyanate structures. The main types of aliphatic isocyanates are hexamethylene diisocyanate (HDI), isophorone diisocyanate (IPDI), and the hydrogenated version of MDI,4,4′-diisocyanatodicyclohexylmethane (H12MDI).
if you have any question about product detail please
MARKETING POLE GROUP
Central Office TEL: 0098 5138407354
Email : info@marketingpole.com