POLYVINYL ALCOHOL

INTRODUCTION
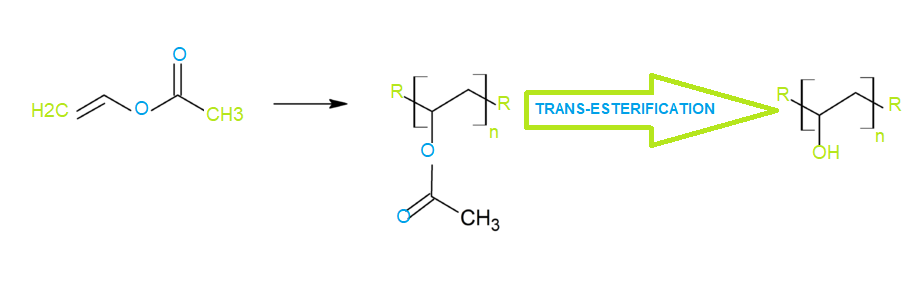
Polyvinyl alcohol (PVOH, PVA, or PVAl) is a water soluble synthetic polymer which is colorless, odorless and water-soluble. It is usually supplied as a powder, granules, or pellets, or sometimes as a solution in water. Polyvinyl alcohol is produced commercially from polyvinyl acetate, usually by a continuous process. The acetate groups are hydrolyzed by ester interchange with methanol in the presence of anhydrous sodium methylate or aqueous sodium hydroxide.
The physical characteristics and its specific functional uses depend on the degree of polymerization and the degree of hydrolysis. Polyvinyl alcohol is classified into two classes namely: partially hydrolyzed and fully hydrolyzed. It is soluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol, but insoluble in other organic solvents. Typically a 5% solution of polyvinyl alcohol exhibits a pH in the range of 5.0 to 6.5. Polyvinyl alcohol has a melting point of 180 to 190°C. It has a molecular weight of between 26,300 and 30,000, and a degree of hydrolysis of 86.5 to 89%.
The wide range of chemical and physical properties of PVA resins has led to their broad industrial use. They are excellent adhesives and highly resistant to solvents, oil, and grease. Poly(vinyl alcohol) forms tough, clear films that have high tensile strength and abrasion resistance. Its oxygen-barrier qualities are superior to those of any known polymer. PVA also contributes to emulsification and stabilization of aqueous dispersions. Some other uses are in textile and paper sizing, adhesives, and emulsion polymerization.

Significant volumes are also used in such diverse applications as joint cements for building construction, water soluble film for hospital laundry bags, emulsifiers in cosmetics, temporary protective films to prevent scratching of highly polished surfaces, and soil binding to control erosion, unit- dose pharmaceuticals, water treatment chemicals, “artificial tears” used to treat dry eyes, contact lens lubricants, transfer printing, agrochemicals, embroidery and dust abatement. Poly(vinyl alcohol) is an intermediate in the production of poly(vinyl butyral), the adhesive interlayer in laminated safety glass. It can also be used as a thickener in wall paints, paper coatings, Polyvinyl alcohol forms a very good adhesive film and is well soluble in water , and it is also used as an additive or modifier in polyvinyl acetate-based adhesives, emulsions and dispersions. Partially hydrolyzed PVA is used in the foods, It is used as a moisture barrier film for food supplement tablets and for foods that contain inclusions or dry food with inclusions that need to be protected from moisture uptake.
if you have any question about product detail please
MARKETING POLE GROUP
Central Office TEL: 0098 5138407354
Email : info@marketingpole.com